AGRICULTURE
Changing the face of farming in India
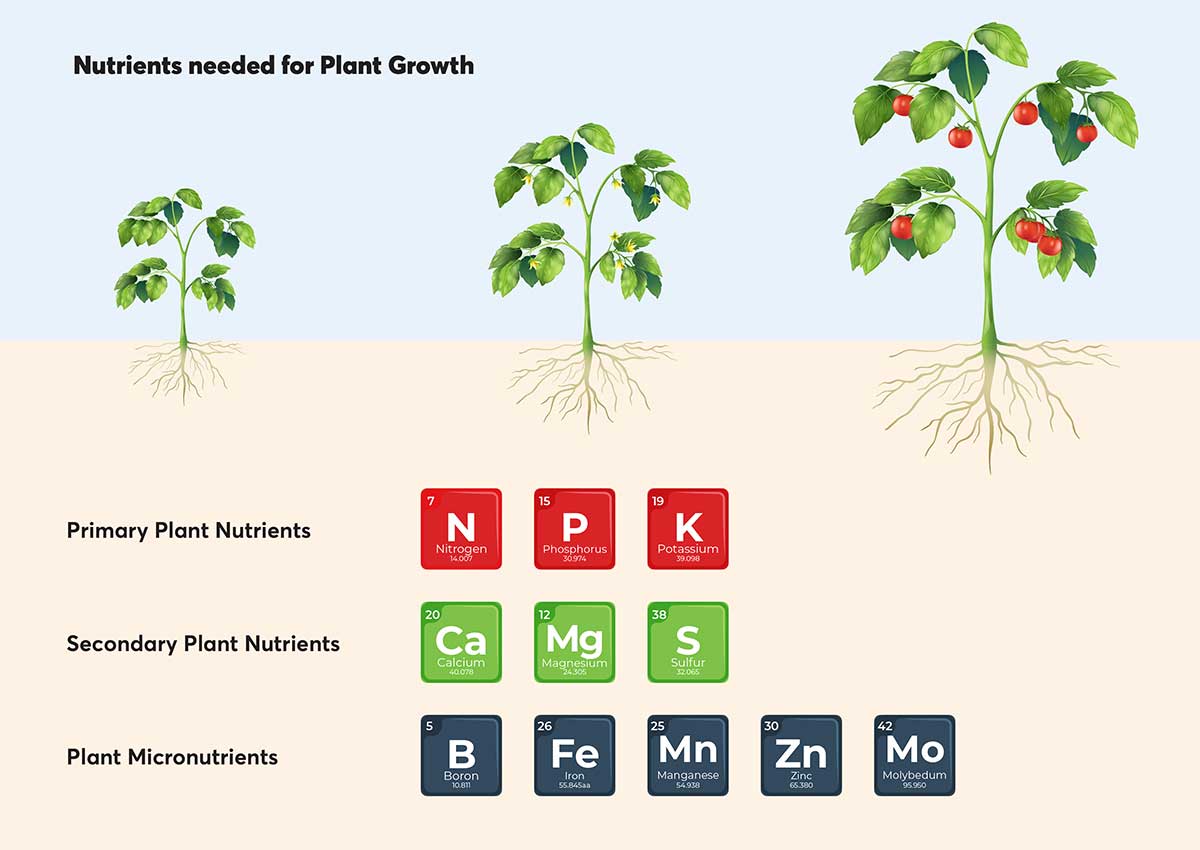
MICRONUTRIENTS 




Quick Facts
- Micronutrients are a fine blend of minerals including Zinc, Copper, Manganese, Iron, Boron etc., which play an important role on plant growth, development and productivity.
- Zinc is required in the synthesis of tryptophan, which in turn is necessary for the formation of indole acetic acid in plants and plays key role in RNA and protein synthesis. Zn is also an essential component of several metalloid-enzymes in plants (variety dehydrogenases) and therefore is necessary for several different function in plant metabolism. An excess of Zinc leads to iron deficiency and reduces manganese absorption. Whereas a deficiency of Zinc causes stunted and mottled growth of the leaves.
- Copper activates enzymes and catalyses reactions in several plant-growth processes. It is essential in several plant enzyme systems involved in photosynthesis. Copper also serves to intensify flavour and colour in vegetables and colour in flowers. An excess of copper encourages iron deficiency in plants while a deficiency leads to poor growth, delayed flowering and plant fertility.
- Manganese is a major contributor to various biological systems in plants including photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen assimilation. Manganese is also involved in pollen germination, pollen tube growth, root cell elongation and resistance to root pathogens. A deficiency of Manganese affects the water balance of the plant and appears as chlorosis in leaves and the tissue of the fruit.
- Boron assists plants in the growth and cell development. Adequate levels of Boron help in better flowering, nodule formation and plays a vital role in seeds and fruit development. Boron is necessary in the synthesis of one of the bases for RNA formation and in cellular activities. Boron has also been associated with lignin synthesis, activities of certain enzymes, seed and cell wall formation, and sugar transport. The deficiency of Boron is the most widespread micronutrient deficiency across the world and it leads to slow down of water absorption, root development, and sugar translocation in plants.